Explore the innovation, impact, and future focus of computer technology, covering AI, quantum computing, cybersecurity, and IoT advancements.
Introduction
In the 21st century, computer technology has become the driving force behind nearly every aspect of modern life. From the smartphones in our pockets to the supercomputers predicting global weather patterns, computers have transformed how we communicate, work, learn, and innovate.
The rapid evolution of computing—from room-sized mainframes to AI-powered neural networks—has reshaped industries, economies, and even human behavior. Artificial Intelligence (AI), quantum computing, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are no longer futuristic concepts but real-world technologies accelerating progress in healthcare, finance, education, and beyond.
This article dives deep into the innovation, societal impact, and future focus of computer technology, exploring:
- How computing has evolved from mechanical calculators to self-learning algorithms
- Breakthrough innovations like AI, cloud computing, and quantum processing
- The profound impact on businesses, healthcare, and daily life
- What’s next? Emerging trends like edge computing, 5G, and ethical AI
As we stand at the brink of a new technological revolution, understanding these advancements is crucial—not just for tech professionals, but for anyone navigating our increasingly digital world.
2. The Evolution of Computer Technology
The journey of computer technology is a remarkable saga of human ingenuity, spanning centuries of innovation. What began as simple counting tools has evolved into artificial intelligence systems capable of mimicking human thought. This section explores the key milestones in computing history, highlighting how each breakthrough paved the way for today’s digital revolution.
The Five Generations of Computing: A Transformational Timeline
1. Mechanical Era (Pre-20th Century)
- Abacus (3000 BCE): The world’s first “computer,” used for basic arithmetic.
- Pascaline (1642): Blaise Pascal’s mechanical calculator for addition/subtraction.
- Analytical Engine (1837): Charles Babbage’s design for the first programmable computer (never built)
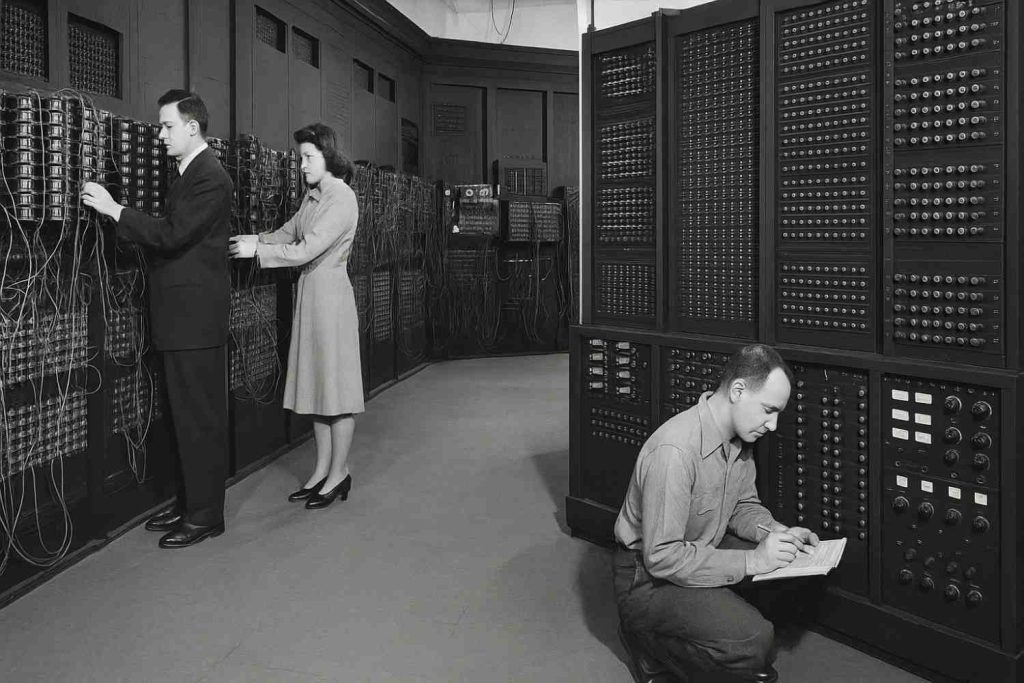
2. First Generation (1940s-1950s): Vacuum Tube Computers
- ENIAC (1946): The first electronic general-purpose computer, weighing 27 tons.
- Colossus (1943): British code-breaking machine used in WWII.
- Key Features:
- Room-sized machines
- Consumed enormous power
- Programmed via punch cards

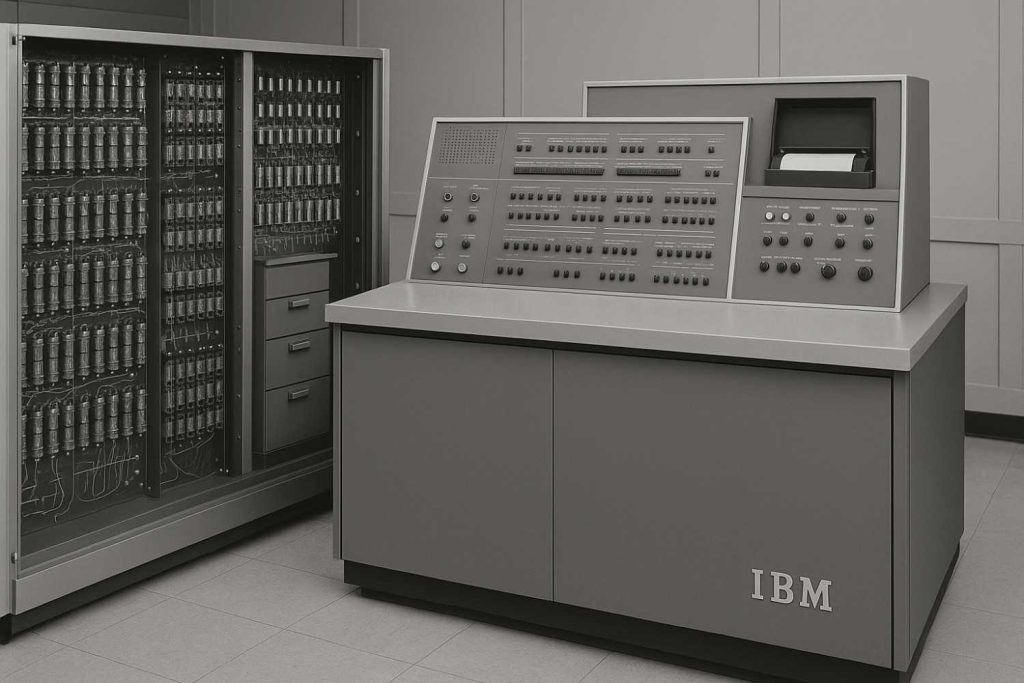
3. Second Generation (1950s-1960s): Transistors Replace Tubes
- IBM 1401 (1959): First commercially successful transistorized computer.
- UNIVAC (1951): First mass-produced computer (used for U.S. census).
- Key Advances:
- 100x smaller than vacuum tubes
- More reliable and energy-efficient
- Early programming languages (COBOL, FORTRAN)

4. Third Generation (1960s-1970s): Integrated Circuits & Minicomputers
- IBM System/360 (1964): First family of compatible computers.
- ARPANET (1969): Precursor to the modern Internet.
- Key Innovations:
- Silicon chips replaced individual transistors
- Birth of personal computing (Altair 8800)
- Graphical user interfaces (Xerox Alto)

5. Fourth Generation (1970s-Present): Microprocessors & Personal Computing
- Intel 4004 (1971): First commercial microprocessor.
- Apple II (1977) & IBM PC (1981): Made computers household items.
- Internet Boom (1990s): World Wide Web (Tim Berners-Lee, 1989).
- Mobile Revolution (2000s): Smartphones (iPhone, 2007) and cloud computing.

3. Key Innovations in Computer Technology
The relentless advancement of computer technology has given birth to revolutionary innovations that are redefining industries, economies, and daily life. From artificial intelligence to quantum supremacy, these breakthroughs push the boundaries of what machines can achieve. This section explores the most transformative computing innovations, their real-world applications, and how they are driving the next wave of digital transformation.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML)
Why It’s Revolutionary:
AI enables machines to learn, reason, and make decisions like humans—but at unprecedented speed and scale.
Key Developments:
- Deep Learning (2010s): Neural networks powering image/speech recognition (e.g., Google DeepMind, OpenAI GPT-4).
- Generative AI (2020s): ChatGPT, DALL·E, and Midjourney create human-like text, art, and code.
- Autonomous AI: Self-driving cars (Tesla, Waymo) and robotic automation (Boston Dynamics).
Impact:
✔ Healthcare: AI diagnoses diseases (IBM Watson) and accelerates drug discovery.
✔ Finance: Fraud detection (Mastercard AI) and algorithmic trading.
✔ Customer Service: Chatbots (Zendesk, Intercom) handle 80% of routine queries.

2. Quantum Computing
Why It’s Revolutionary:
Unlike classical bits (0 or 1), quantum bits (qubits) exist in multiple states at once, solving problems millions of times faster.
Key Developments:
- Google’s Quantum Supremacy (2019): Solved a task in 200 seconds that would take a supercomputer 10,000 years.
- IBM Quantum Roadmap (2023): 1,000+ qubit processors by 2025.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: Preparing for unhackable encryption.
Impact:
✔ Drug Discovery: Simulating molecular interactions in seconds.
✔ Climate Modeling: Optimizing carbon capture and renewable energy.
✔ Financial Risk Analysis: Predicting market crashes with extreme precision.

3. Blockchain & Decentralized Systems
Why It’s Revolutionary:
Blockchain creates tamper-proof, transparent ledgers without central authorities.
Key Developments:
- Bitcoin (2009): First decentralized cryptocurrency.
- Ethereum Smart Contracts (2015): Self-executing agreements (DeFi, NFTs).
- Web3 (2020s): Decentralized internet (IPFS, DAOs).
Impact:
✔ Supply Chains: Walmart tracks food safety via blockchain.
✔ Voting Systems: Secure, fraud-proof digital elections (Estonia’s e-voting).
✔ Digital Identity: Self-sovereign IDs (Microsoft ION).
4. Neuromorphic Computing
Why It’s Revolutionary:
Mimics the human brain’s architecture for ultra-efficient AI processing.
Key Developments:
- Intel Loihi (2021): Self-learning neuromorphic chip.
- SpiNNaker (2020): Supercomputer simulating 1 billion neurons.
Impact:
✔ Edge AI: Real-time decision-making in drones and IoT devices.
✔ Medical Prosthetics: Brain-controlled robotic limbs.
5. 5G & Next-Gen Connectivity
Why It’s Revolutionary:
100x faster than 4G, enabling real-time IoT, AR/VR, and autonomous systems.
Key Developments:
- T-Mobile’s Nationwide 5G (2020): Sub-6GHz and mmWave speeds.
- 6G Research (2030s): Terahertz frequencies and AI-integrated networks.
Impact:
✔ Smart Cities: Traffic lights adjust in real-time to congestion.
✔ Telemedicine: Remote surgeries with zero lag (5G robotic surgery).
Conclusion: The Future Is Being Written Now
These innovations are not just incremental upgrades—they are paradigm shifts reshaping reality. As AI, quantum, and blockchain mature, their convergence will unlock possibilities we’ve only imagined.
Key Takeaways:
✔ AI is the new electricity—powering everything from healthcare to creativity.
✔ Quantum computing will crack problems deemed unsolvable.
✔ Blockchain = Trustless systems, from money to voting.
✔ 6G and neuromorphic chips will blur the line between human and machine intelligence.
The Profound Impact of Computer Technology on Society
Computer technology has undeniably reshaped every facet of our lives, transforming societies globally in ways that were unimaginable just a few decades ago. From how we work and communicate to how we learn and entertain ourselves, the digital revolution has left an indelible mark, bringing both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges.
Communication and Connection Revolutionized

The Profound Impact of Computer Technology on Society
Computer technology has undeniably reshaped every facet of our lives, transforming societies globally in ways that were unimaginable just a few decades ago. From how we work and communicate to how we learn and entertain ourselves, the digital revolution has left an indelible mark, bringing both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges.
Communication and Connection Revolutionized
Perhaps the most visible impact of computer technology is the revolution in communication. The internet, powered by computers, has obliterated geographical barriers, enabling instant global communication. Social media platforms, messaging apps, and video conferencing tools allow individuals to connect with friends, family, and colleagues across continents in real-time. This interconnectedness has fostered new forms of communities, expanded social circles, and facilitated cultural exchange on an unprecedented scale. However, this shift towards digital interaction has also raised concerns about decreased face-to-face interaction, potential social isolation, and the rise of issues like cyberbullying and the spread of misinformation.
Economic Transformation and the Digital Economy
Computer technology has been a primary driver of economic growth and transformation. It has served as the bedrock of the digital economy, where data is a valuable currency. Businesses worldwide rely on computers to collect, process, and analyze vast amounts of data, leading to informed decision-making and innovation. E-commerce, online marketplaces, and digital payment systems have flourished, expanding market access globally and streamlining transactions.
However, this economic shift has also led to job displacement in certain sectors due to automation, as robots and software take over tasks previously performed by humans. This necessitates a continuous re-skilling of the workforce and the creation of new job opportunities in emerging fields like artificial intelligence and robotics. The economic landscape is constantly evolving, demanding adaptability and continuous learning.
Education Redefined and Empowered
The realm of education has been profoundly transformed by computer technology. Online learning platforms, digital resources, and educational software have made knowledge more accessible and flexible than ever before. Students can now learn anytime, anywhere, at their own pace. Interactive learning technologies, such as simulations, virtual reality, and AI-powered tutors, create engaging and personalized learning experiences. While this has expanded access to education globally, it also highlights the digital divide, where unequal access to technology can exacerbate existing inequalities
FAQs
Q1: What is the next big thing in computer technology? A: Quantum computing is poised to revolutionize computational power, enabling solutions to problems currently intractable for even the most powerful supercomputers. Alongside this, continuous and rapid advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI), particularly in areas like generative AI, machine learning, and natural language processing, are leading the next wave of transformative technological breakthroughs.
Q2: How does computer technology affect jobs? A: Computer technology’s impact on jobs is multifaceted. While automation, driven by AI and robotics, is leading to the replacement of certain routine or manual jobs, particularly in manufacturing and administrative tasks, it simultaneously creates entirely new roles and industries. There’s a growing demand for professionals in areas such as AI development, data science, cybersecurity, cloud computing, and digital marketing. The shift emphasizes the need for continuous skill development and adaptation to a changing workforce landscape.
Q3: Is cybersecurity a growing concern? A: Absolutely, yes. With the increasing digitalization of nearly every aspect of life – from personal data and financial transactions to critical infrastructure and government operations – cybersecurity has become more critical than ever. The frequency, sophistication, and impact of cyber threats, including data breaches, ransomware attacks, and phishing scams, are on a constant upward trend. Protecting digital assets and ensuring online safety is a paramount concern for individuals, businesses, and nations worldwide.
Conclusion
Computer technology isn’t just a fleeting trend; it’s a fundamental force that continues to weave itself deeper into the fabric of our existence, constantly reshaping our future with groundbreaking innovations. From the microscopic silicon chips powering our everyday devices to the vast, interconnected networks spanning the globe, its influence is all-encompassing, touching every industry, every economy, and every facet of our daily lives. We’re witnessing not just progress, but a continuous redefinition of what’s possible.
Check in Best Electric Scooter